Soft 404 errors can be a frustrating issue for website owners and SEO professionals alike. These errors occur when a webpage appears to be functional with a 200 OK status but actually presents a message indicating that the content is not available. This discrepancy can lead to confusion for both users and search engines, ultimately impacting your site’s performance in search results.
Understanding soft 404 errors
A soft 404 error happens when a server responds with a 200 OK status for a page that should return a 404 (Not Found) status. This situation misleads search engines into thinking the page is valid while users encounter a message indicating that the content is not found. According to Google, this can lead to issues with indexing and negatively affect your website’s rankings.
To better understand soft 404 errors, it’s essential to recognize their common causes. Poor server configurations often lead to these errors, as some servers are set up to return a 200 status for pages that do not exist. Additionally, pages with very little content may also be flagged as soft 404s by crawlers, as they do not provide sufficient value or context.
Sometimes, such errors may concern listings that are changing – for example, if part of the records disappears from the list for a given category – Google may classify the page as a soft 404. Therefore, if the content reappears, you should resubmit the URL for validation.
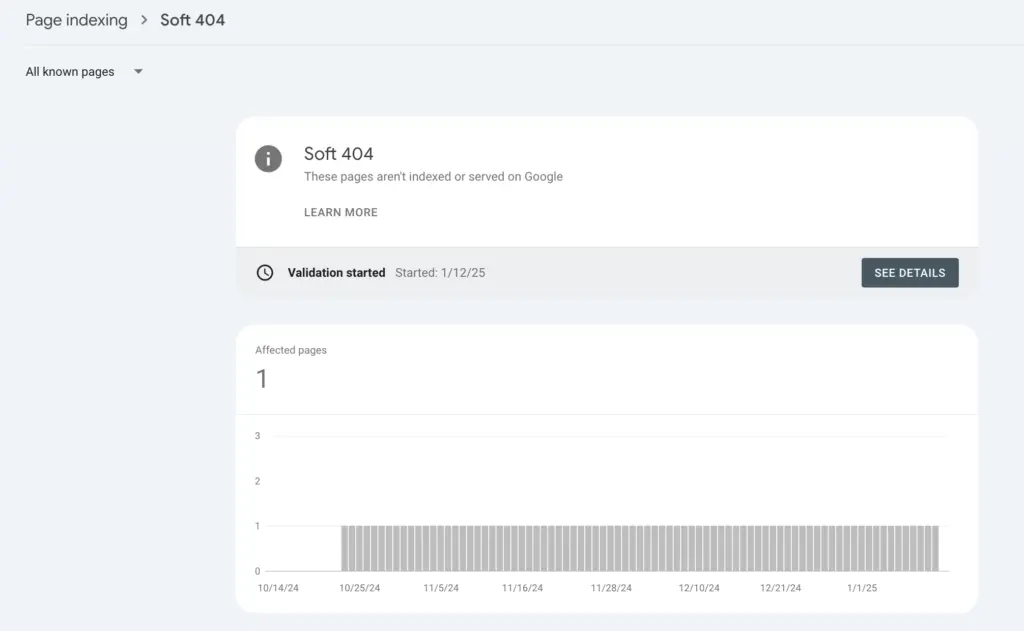
Identifying soft 404 errors in Google Search Console
The first step in addressing soft 404 errors is to identify them within Google Search Console. Navigate to the “Idexing” report (”Pages”) and look for any URLs marked as soft 404s. This section will provide insights into which pages are causing issues and why they are being flagged.
Once you have identified the problematic URLs, it’s crucial to verify their validity. Check if these pages genuinely contain content or if they are mistakenly marked as soft 404s. If a page is indeed non-existent or should return a different status, you will need to take appropriate action.
WYIMEK: Remember that the ideal tool for managing errors reported by GSC is Revamper11. Read what it is and how to use it.
Fixing soft 404 errors
To resolve soft 404 errors effectively, follow these best practices:
Change response codes
For pages that no longer exist, ensure they return a proper 404 status code instead of misleading users with a 200 response. This clear communication informs both users and search engines that the content is unavailable.
Enhance thin content
If you have pages that are valid but flagged as soft 404s due to insufficient content, consider enhancing them with relevant information, images, and links. This improvement signals their value and helps prevent misclassification.
Redirect wisely
If you have removed content but want to direct users elsewhere, use appropriate redirects (301) to guide them to relevant pages instead of leading them back to the homepage or unrelated content.
Regular audits
Conduct regular audits of your website using tools like Google Search Console to monitor for new soft 404 errors and address them promptly.
Preventing future soft 404 errors
To avoid encountering soft 404 errors in the future, implement proactive measures:
– Ensure your server configurations are correctly set up to return appropriate HTTP status codes.
– Regularly review your website’s content for quality and relevance.
– Utilize custom error pages that guide users back to useful sections of your site rather than leaving them at a dead end.
By following these recommendations, you can maintain the integrity of your website’s indexing and improve user experience.
Citations:
https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/7440203?hl=en
https://prerender.io/blog/soft-404
https://ziptie.dev/blog/soft-404-explained
https://neilpatel.com/blog/soft-404s
https://yoast.com/what-is-a-soft-404-error
https://www.searchenginejournal.com/technical-seo/404-vs-soft-404-errors
